Abstract
Background: The hypomethylating agents (HMAs) azacitidine and decitabine have been increasingly used in the frontline setting for elderly and/or unfit patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). While these therapies are oftentimes used in the palliative setting, HMAs have also been used with curative intent in some patients, as a bridge to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). It is well known that 4-6 cycles of HMA therapy can be necessary to achieve a response; however, it is still common in practice for treating physicians to stop HMAs earlier when a rapid response is not observed. Few studies have investigated time to response in the setting of frontline HMA treatment for AML.
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated all patients who were initiated on frontline HMAs for AML at our institution from September 2013 to April 2018. HMAs were administered without dose reduction or treatment delays. Responses were evaluated and categorized as hematologic response (HR; defined by neutrophils > 1000/µL, platelets > 100k/µL, transfusion independence, and no peripheral blasts), complete remission (CR), CR with incomplete platelet recovery (CRp), CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi), and no response. Patient, cytogenetic, and treatment characteristics were summarized and described. We evaluated patients exhibiting a response before receiving 4 cycles of HMA therapy ("early" responders) and compared these patients to those achieving a response after receiving at least 4 cycles of HMA ("late" responders). The Kaplan-Meier method estimated overall survival (OS). Odds of early response were estimated with logistic regression models.
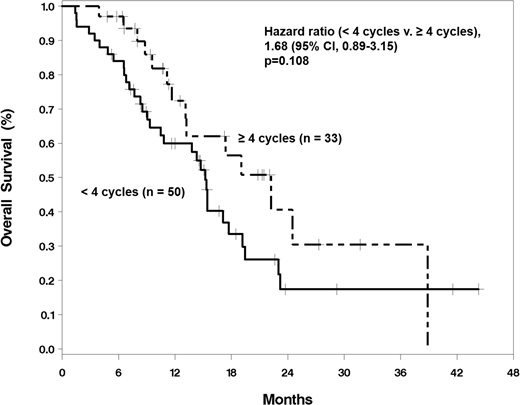
Results: During the study period, 137 patients received frontline HMAs. 122 (89.1%) patients received azacitidine, and 15 (10.9%) were treated with decitabine. Mean age at HMA start was 70.1 years (range 39.8-94.3). Most patients (62.8%) were male, and most (77.4%) were Caucasian. 21 (15.3%) patients were NCCN favorable-risk, 52 (38.0%) were intermediate-risk, and 64 (46.7%) were poor-risk. At first testing, 21.4% of the patients were positive for the FLT3/ITD mutation, 0.8% the FLT3/TKD mutation, and 21.4% the NPM1 mutation. Some patients received concomitant therapies along with the HMA; these included hydroxyurea, lenalidomide, and sorafenib. Median survival in the entire population was 11.6 (95% CI 8.3, 15.2) months. Overall response rate (ORR) was 60.6%. Among responders, 80.7% achieved HR as their first response; 19.3% were first noted to have marrow responses (1.2% CR, 4.8% CRp, and 13.3% CRi). Most patients did not undergo bone marrow evaluation to assess response. Among responding patients, 60.2% responded "early", whereas 39.8% responded "late". Median overall survival was 15.2 (9.3, 17.7) months in early responders, and 22.2 (11.7, 38.9) months in late responders. There was no difference in survival between the groups (p=0.108, log-rank test; Figure 1), although there was a trend toward improved survival in late responders. Nineteen patients underwent allogeneic HCT. Time to response was not associated with odds of receiving HCT (p=0.812).
Conclusions: HMAs have a high ORR as frontline therapy in elderly and unfit AML patients. Among AML patients receiving frontline HMAs, later responders have equivalent survival to earlier responders. Physicians should consider exercising patience when treating AML patients with HMAs. These findings warrant validation in a larger, prospective study.
Avalos:Juno: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Grunwald:Alexion: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Ariad: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Forma Therapeutics: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Cardinal Health: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Medtronic: Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal